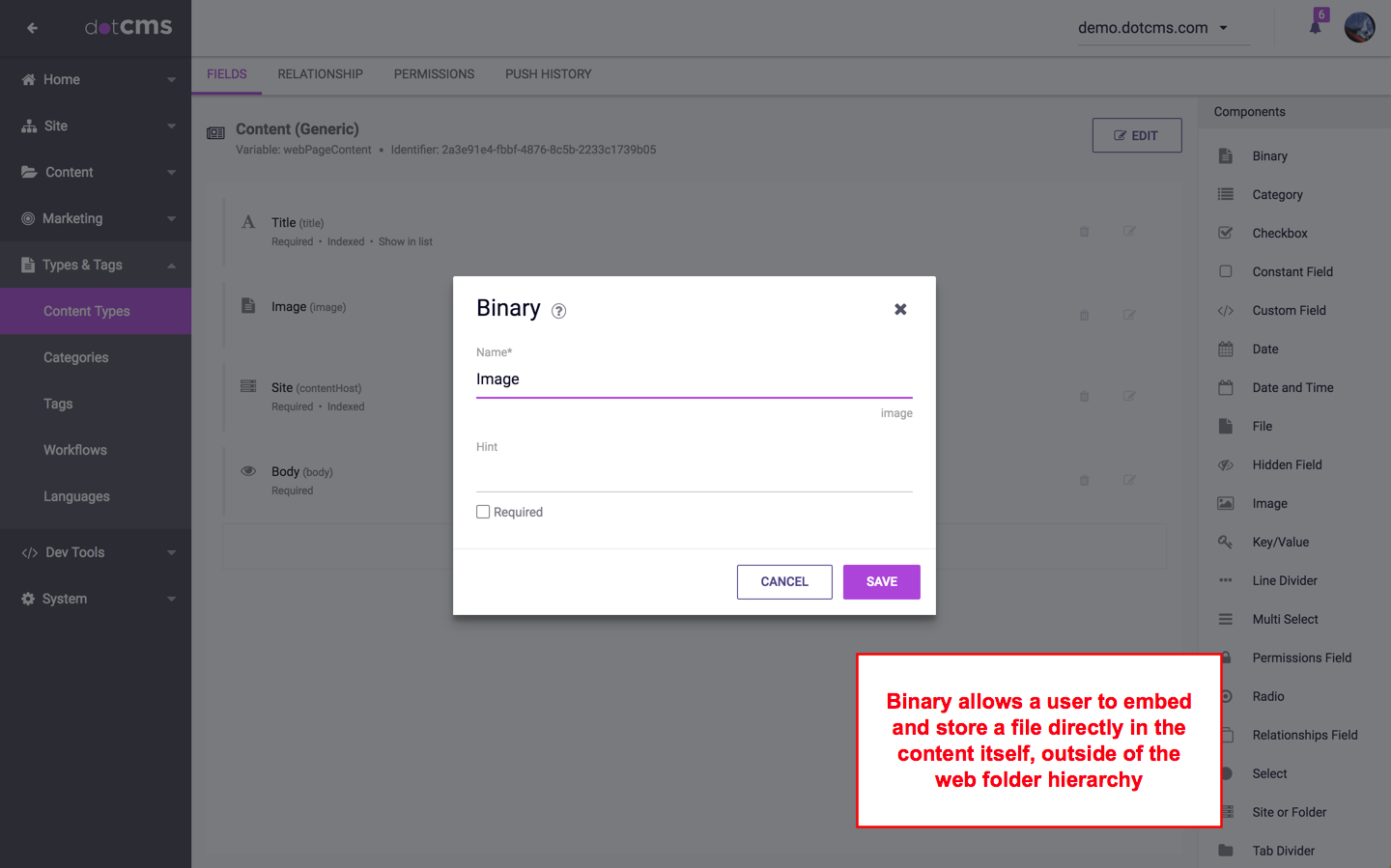
Adding a Binary Field to a Content Type allows the user to embed and store any file directly in the content itself without placing that file in the Site Browser hierarchy.
Comparison of Binary Fields vs. Image and File Fields
You may add images or files to a Content Type using either Binary fields, or the Image and File fields. The difference is that Binary fields store the file or image inside the content itself, while Image and File fields store the file or image as a separate content item, which is then linked to from the Image or File field.
Binary Field Advantages
The advantages of using a Binary field instead of an Image or File field are:
- The file can be edited from the contentlet itself.
- Only users that have permissions to view or edit the content will have access to view or modify the file associated with the content.
- Improved performance with dynamic pulls.
Binary Field Disadvantages
The disadvantages of using Binary field are:
- Since the file does not exist in any folder location within the Site Browser, a directory path cannot be passed to a photo gallery, video gallery, file repository, etc.
- The file can not be re-used in multiple content items.
- The file can't be displayed in bulk (by viewing a site or folder containing multiple files).
Field Variables
You may add Field Variables to Binary fields to limit both the size and types of files which can be uploaded:
| Field Variable Key | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
accept | application/pdf,image/* | A comma-separated whitelist of mimeTypes allowed for uploaded files.
|
maxFileLength | 1024 | The maximum size of uploaded files, in bytes. |
Notes on API Usage
Setting Binary Field Content Via API
Using the Workflow REST API, it is possible to populate a Binary field in several ways, corresponding to three subsections of the linked passage. These subsections detail uploading a single file, uploading multiple files, or populating a (plaintext) File Asset via string.
Metadata Access Through Content Object
As of dotCMS 23.01, it is possible to access a Binary field's metadata by way of its contentlet through REST API calls. This can be surfaced through the Page API, Content API, or Elastic Search API.
When retrieved in this way, each Binary field will be paired with a metadata property within the entity object, named similarly to the Binary field itself. For instance, if your Content Type has three Binary fields named bin1, binary2, and doc, there will be three attendant properties entitled bin1MetaData, binary2MetaData, and docMetaData, with contents along the lines shown below:
{
"entity": {
...
"binary2": "/dA/2b928d273d02eff4ee4ff257d15d06a6/binary2/Logo_Purple_Background.jpg",
"binary2ContentAsset": "2b928d273d02eff4ee4ff257d15d06a6/binary2",
"binary2MetaData": {
"contentType": "image/jpeg",
"fileSize": 115305,
"height": 640,
"isImage": true,
"length": 115305,
"modDate": 1695995714593,
"name": "Logo_Purple_Background.jpg",
"sha256": "2d84764d51de15cedec3ab2a1c79c1a6e21de2fea321571a4da302a39d192d6d",
"title": "Logo_Purple_Background.jpg",
"version": 20220201,
"width": 1630
},
"binary2Version": "/dA/4d7cdeb3-fd03-417c-b12b-4be8447122e9/binary2/Logo_Purple_Background.jpg",
...
}
...
}